Welcome to my blog post. Today, I’m going to talk about whether an LFP battery is suitable for use in headlamps and flashlights.
LFP batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and superior safety compared to other lithium-ion batteries. The graph below from Google Trends shows how popular the LFP battery has been since 2021!

What is the LFP battery?
LFP battery is short for lithium ferro-phosphate battery. It’s also called Lithium Iron Phosphate battery, LiFePO4 battery, or Li-IP battery.
The LFP battery is a lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the cathode material and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as the anode. (Refer to WIKI) . In short, LFP is a Li-Ion battery, but not all Li-Ions are LFPs.
History of LFP battery (LiFePO4)
LFP (lithium iron phosphate) batteries have a relatively short history compared to other types of batteries. Still, they have gained popularity due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and safety features.
The development of LFP batteries began in the late 1990s when Dr. John Goodenough, one of the co-inventors of the lithium-ion battery, started researching ways to improve its performance. Goodenough’s research team discovered that using iron phosphate as a cathode material could increase the battery’s safety, stability, and cycle life.
In 1996, Goodenough’s team published a paper describing a new type of cathode material for lithium-ion batteries that used iron phosphate instead of cobalt oxide. This was the first major breakthrough in LFP battery technology and paved the way for further research and development.
Over the next decade, other researchers and manufacturers refined LFP battery technology. In 2004, A123 Systems, a company founded by Goodenough’s former student, developed the first commercially available LFP battery for electric vehicles. This battery had a higher energy density and longer cycle life than other types of batteries, making it an attractive option for electric vehicle manufacturers.
Since then, LFP batteries have become increasingly popular in various applications, including electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and portable electronics. They are known for their high safety standards, thermal stability, and resistance to thermal runaway, which is a common problem with other lithium-ion batteries.

Advantages of LFP battery
There are several advantages of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, also known as LFP batteries, which are listed below, along with their explanations:
Safety:
LiFePO4 batteries are considered one of the safest lithium-ion battery chemistries available because they are less prone to thermal runaway. This dangerous condition can occur when a battery overheats.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have a stable structure. And they are less reactive compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries. They are less likely to undergo thermal runaway, a self-accelerating reaction that can lead to a fire or explosion.
Fast charging:
LiFePO4 batteries can be charged quickly without significantly degrading capacity or performance.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have a high charge acceptance, which means they can accept a high current during charging without significant degradation in their capacity or performance. This allows them to be charged quickly, making them suitable for applications where fast charging is important, such as electric vehicles.
Low self-discharge rate:
LiFePO4 batteries have a low self-discharge rate, which means they can hold their charge for long periods without significant loss of capacity.
Also, the batteries show no memory effects, and because of the low self-discharge (<3% per month), you can store them for longer.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have a low self-discharge rate, meaning they can hold their charge for extended periods without significant loss of capacity. They are ideal for applications where the battery is not frequently used or needs to be stored for long periods, such as backup power systems.
Long cycle life:
LiFePO4 batteries can withstand many charge-discharge cycles without significant degradation in their capacity or performance.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have a unique crystal structure that enables them to store and release energy without significant degradation over time. They are ideal for applications that require long cycle life, such as electric vehicles and stationary energy storage systems.
Environmental friendliness:
LiFePO4 batteries are environmentally friendly because they do not contain toxic metals such as cobalt or nickel.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries use iron as their cathode material, which is abundant and non-toxic. They are more environmentally friendly than other lithium-ion battery chemistries using toxic metals such as cobalt or nickel.
High-temperature performance:
LiFePO4 batteries can operate at high temperatures without significantly impacting their performance or safety.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have high thermal stability and can operate at temperatures up to 60°C without significant degradation in their performance or safety. They are suitable for applications in hot climates or where high ambient temperatures are expected.
Low maintenance:
LFP batteries (LiFePO4) don’t require active maintenance to extend their service life.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries do not require regular balancing or maintenance, as their internal resistance is low and do not generate significant amounts of heat or gas during operation. This makes them a low-maintenance option for applications where regular maintenance may be difficult or impractical.
Resistance to overcharging:
LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to overcharging than other lithium-ion battery chemistries.
Explanation: LiFePO4 batteries have a low voltage of 3.2 volts per cell, which means they are less likely to overcharge and suffer from damage. This makes them a safer option for applications where overcharging may occur.
Disadvantages of LFP Batteries
Lower energy density:
LFP batteries have a lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) and nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA). This means they have a lower energy storage capacity, which may limit their use in applications requiring higher energy density.
Also, the batteries show no memory effects, and because of the low self-discharge (<3% per month), you can store them for longer.
Higher upfront cost:
LFP batteries can be more expensive than other lithium-ion batteries. However, the long cycle life and low maintenance requirements can offset this initial cost over the battery’s life.
Limited temperature range:
LFP batteries perform best in moderate temperatures between 20-40°C (68-104°F). Outside of this range, their performance can be significantly affected, which may limit their use in specific applications.
Uses of LFP battery
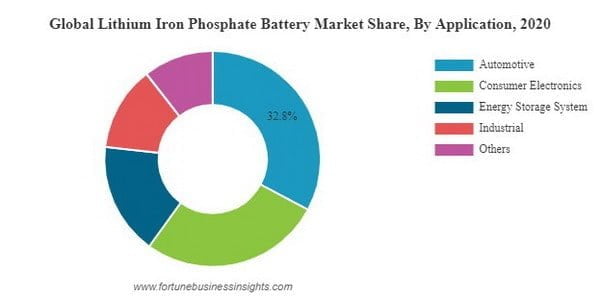
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have a variety of uses due to their unique characteristics and advantages over other types of batteries. Here are some expected benefits of LFP batteries:
Electric Vehicles
LFP batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs) due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and improved safety compared to lithium-ion batteries. They can also be charged quickly and are more resistant to high temperatures, making them ideal for EVs.
Renewable Energy Storage
LFP batteries are also used to store energy generated by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. They can be charged during periods of low demand and discharged during periods of high demand, helping to balance the electricity grid and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Backup Power
LFP batteries can be a backup power source for homes, businesses, and other critical infrastructure. They can be connected to a solar panel system or an electrical grid to provide uninterrupted power during a blackout or different emergencies.
Consumer Electronics
LFP batteries are used in various consumer electronics such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets due to their high energy density, lightweight, and safety.
Conclusions
Overall, LFP batteries are the most popular battery because of their safety. They have gained considerable market acceptance. LFP batteries are now mainly used for perfect power for electronic vehicles. But the LFP battery is ideal for LED headlamps as it’s less heating.
Due to their low energy density, you can only find a few LFP battery flashlights in the market now. But some manufacturers, such as Rivian and Maglite, have taken the bold step of using LFP batteries to power their torches.
As long as the main disadvantage of low energy density is worked out, the LFP battery development prospects are limitless. Let’s keep an eye on it.


